The hydrosphere is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of the earth. It has been estimated that there are 1386 million cubic kilometres of water on earth. This includes water in liquid and frozen forms in groundwater, oceans, lakes and streams. Approximately 75% of Earth’s surface, an area of some 361 million square kilometres, is covered by ocean.
The hydrological cycle transfers water from one state or reservoir to another. Reservoirs include atmospheric moisture including snow, rain and clouds, streams, oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, subterranean aquifers, polar ice caps and saturated soil.

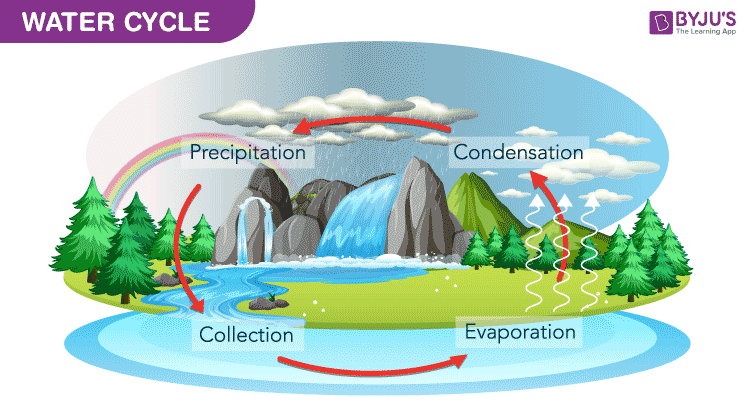
In fact, Solar energy is the source of heat and light and gravity causes the transfer from one state to another over periods from hours to thousands of years. Most evaporation comes from the oceans and is returned to the earth as snow or rain.
It consists of all bodies of water, icebergs and water vapour in the earth’s atmosphere. Oceans contain 97 per cent of water in the hydrosphere, while rivers, lakes and other water bodies on land and underground water contains a small percentage of total water in the hydrosphere.
Here is the importance of the layer-
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more Physics concepts with the help of interactive video lessons.
The hydrosphere is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of the earth. It has been estimated that there are 1386 million cubic kilometres of water on earth.
Atmosphere is a protective layer of gases that shelters all life on Earth, keeping temperatures within a relatively small range and blocking out harmful rays of sunlight.
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth.
Water has a property to transition into different states of matter. On heating, water turns into its gaseous state and forms vapours. Water vapours thus formed are carried away by air and are not visible. Hence water seems to disappear from rooftops and roads. This process is called evaporation.
The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell on Earth. It is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.